Blogs
Articles

How to Build AI Research Agents: A Developer's Guide to Implementation
AI research agents reshape how businesses spot sales opportunities. These autonomous systems scan thousands of online sources with up-to-the-minute data analysis and detect buying signals that human researchers might overlook. The global AI market will reach $190.61 billion by 2025, with a CAGR of 36.62% from 2018 to 2025. Companies are adopting this technology faster to stay ahead of competition.
Autonomous AI research agents bring remarkable business advantages. Sales teams achieve 3-5x higher conversion rates when these agents detect hiring sprees, funding rounds, and technology changes within 24-48 hours. This becomes crucial since traditional contact databases decay at 25-30% annually. Sales development representatives currently spend 5-10 hours each week researching instead of selling.
This piece walks you through the complete process to build and implement AI research agents. You'll learn about their core architecture, select the right frameworks, and ensure ethical deployment. The guide helps you create powerful research agents that deliver best-in-class insights on any topic.
You'll find the technical foundations to succeed, whether you blend these agents into your sales workflows or build custom research solutions.
What are research agents?
Autonomous systems called research agents automate how we collect and analyze information from various sources like databases, websites, and publications. These smart systems use advanced algorithms to find patterns and insights in big data sets that humans might miss.
Research agents work as information processing powerhouses. They can scan thousands of data sources at once. What would take humans days or weeks to compile, these agents can deliver in detailed intelligence reports within minutes. They also watch data streams constantly and provide up-to-the-minute insights that help make faster decisions.
What are AI Research Agents?
AI research agents stand apart from traditional AI systems. They work as autonomous software entities that can set goals, plan actions, and adapt to feedback while interacting with external environments. These intelligent systems need five key components to deliver their sophisticated capabilities.
The heart of AI research agents lies in their perception module that turns raw data from multiple sources into structured information. A knowledge base serves as both working memory for current tasks and long-term storage that preserves insights between research sessions. The reasoning engine acts as the cognitive center to analyze information, spot patterns, and run iterative planning cycles.
These agents also feature an action generator that turns decisions into concrete operations and a learning module that enhances performance through feedback and self-assessment. This design lets AI research agents back every claim with specific citations and ensures factual accuracy in their analyzes.
The AI agents market reached $3.70 billion in 2023 and experts predict it will grow to $103.60 billion by 2032 (CAGR ≈ 44.9%). Companies that use these technologies see 55% better operational efficiency and save about 35% in costs.
AI research agents remove guesswork by automating data collection, analysis, and reporting. They effectively work as a team of expert analysts available around the clock.
Understanding the Core Architecture of AI Research Agents
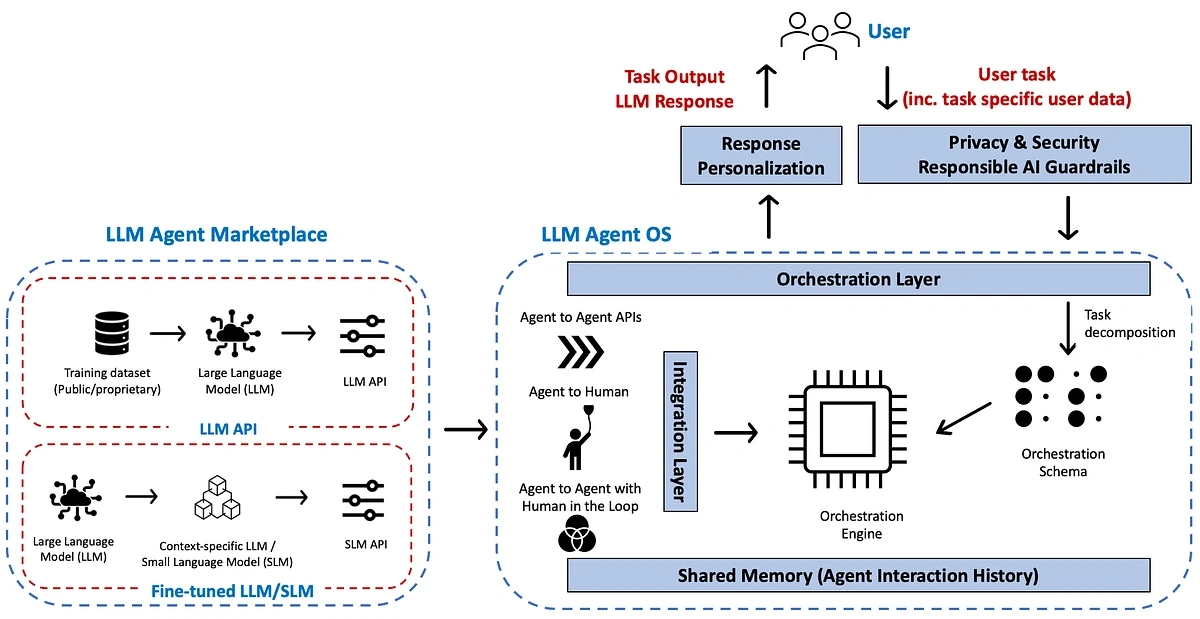
AI research agents work through connected modules that deliver advanced research capabilities. This modular framework helps agents collect information, process data, make decisions, and take action with minimal human input.
Perception and Action Modules in Autonomous Agents
The perception module works like the agent's sensory interface with its environment, transforming raw inputs into structured representations that guide reasoning. It takes in data from text, audio, and sensor signals. The module then extracts features and interprets them to build meaningful models of current situations. The action module turns decisions into real outcomes through three channels: actuators for physical tasks, execution systems for software commands, and tools for special capabilities.
Memory and Knowledge Base Integration
AI research agents need both short-term and long-term memory systems to work well. Short-term memory keeps track of context during tasks, monitors current state, and helps with adaptive planning. Long-term memory stores past data and actions. This helps agents remember what they've learned and apply it to new situations. Good memory management turns basic AI programs into smart agents that learn and maintain continuity between sessions.
Reasoning Engine for Hypothesis Generation
The reasoning engine sits at the agent's core. It reviews context, sets intent, and picks the right actions. Agents use this component to create testable scientific hypotheses by finding patterns, spotting anomalies, and combining knowledge from different fields. The hypothesis-driven approach captures expert knowledge and provides clear reasoning steps to build hypothesis exploratory graphs.
Natural Language Understanding with LLMs
Large Language Models are the foundations of how research agents understand natural language. These models handle text like humans do, process huge amounts of data, and spot complex patterns through reasoning. LLMs help suggest new ideas, write scientific papers, and generate computer code. This leads to better productivity.
Signal Scoring and Relevance Filtering
The last architectural piece focuses on reviewing and filtering relevant information. Real-world agents use feedback through user ratings, ground-truth labels, or automated signal detectors. These signals help retrain systems, tune prompts, or update rewards to boost performance. The system also learns from past mistakes through reflection loops. This makes it more reliable and ensures only the most relevant information reaches decision-making steps.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building AI Research Agents
AI research agents need a structured approach with clear goals and the right tech stack. Let's get into the steps you need to create agents that deliver reliable results.
Defining the Research Scope and Objectives
Your agent needs clear goals from the start. You should map out specific tasks, target users, and research areas the agent will handle. The SMART framework helps create objectives that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. This keeps development focused and prevents feature creep.
Selecting a Foundation Model (e.g., GPT-4, PaLM 2, LLaMA)
The foundation model you pick will affect your agent's capabilities by a lot. Here's what to think about when choosing:
Performance on relevant measurements
Few-shot learning capabilities
Domain knowledge needs
Context window size
Throughput and latency needs
Budget limits
Each model has its own mix of training data quality, tokenization methods, and reasoning abilities. You should test several models in controlled conditions before making your choice.
Data Collection and Preprocessing for Domain Adaptation
Quality data is the foundation of research agents that work well. Build a strong data pipeline with:
Domain-specific documents and knowledge sources
Task demonstrations that show expected behavior
Synthetic data for rare scenarios
Public datasets to increase training data
The data needs proper cleaning to remove duplicates and sensitive information. You should organize everything into consistent formats and structure it into proper training sets.
Training and Fine-Tuning with Domain-Specific Corpora
The training process offers several approaches:
Full fine-tuning to adapt the entire model
Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) with LoRA and QLoRA for quick adaptation
Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) using input-output pairs
A smaller model fine-tuned for your needs often costs less than repeatedly calling large general models through APIs. You'll want a solid evaluation pipeline that combines numbers and human feedback to check performance.
Implementing Prompt Engineering for Task Optimization
Good prompt engineering reshapes the scene. These strategies work best:
Clear goals with action verbs
Context and background information
Few-shot prompting with examples
Precise language
Testing different approaches
Chain-of-thought prompting
Note that effective prompts come from structured thinking that guides the model, not magic words.
Deploying Agents with AutoGen or CrewAI Frameworks
AutoGen or CrewAI frameworks make agent deployment easier. Microsoft Research's AutoGen supports multi-agent workflows through automated chat and shines in LLM research. CrewAI takes a different approach with role-based orchestration where agents have specific jobs and goals. It works great for business processes that need reliability.
AutoGen and CrewAI handle agent teamwork differently. AutoGen uses conversation-driven tasks while CrewAI follows role-oriented patterns. Your choice depends on whether you want controlled workflows or flexible collaboration.
Integration and Workflow Automation in Research Environments
AI research agents need smooth integration with external data sources and systems to realize their full potential. These connections give agents access to real-life information and help create automated workflows that boost productivity.
Connecting Agents to External Knowledge Bases
Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases help AI research agents connect with proprietary information sources and deliver relevant data that improves response accuracy. Agents can search vector stores through Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and include citations that reference original sources.
Real-Time Data Ingestion from APIs and Sensors
Quick data ingestion makes agents more responsive. Agents can access streaming information from websites, mobile apps, transactions, and IoT sensors through sub-second data flow. This immediate context lets AI research agents make decisions with the latest data instead of outdated information.
CRM and Research Tool Integration (e.g., ELNs, LIMS)
AI research agents become more valuable when integrated with CRM systems like Salesforce and HubSpot. These connections provide access to customer data, lead information, and sales pipeline stages. Scientific environments benefit as agents can arrange entire research workflows by launching containerized tools that automate previously manual tasks.
Trigger-Based Automation for Research Workflows
Platforms like Trigger.dev let AI research agents automate workflows based on specific events. The system watches and detects patterns in data and starts processes automatically without constant human oversight. Research pipelines run faster with reliable error handling and clear visibility.
Using RESTful APIs and OAuth 2.0 for Secure Access
Secure integration needs resilient authentication. OAuth 2.0 offers a standardized protocol that authorizes without sharing credentials. This separation of identity from access works perfectly for AI agents that act on behalf of users. Agents can access external services securely while maintaining detailed permission controls with proper implementation.
What are the Best Practices and Tools for Scalable Agent Development?
AI research agents need reliable tools and proven methods to work well in production environments. Here's a look at the frameworks and methods that are the foundations of good agent development.
Using mlgym to Measure AI Research Agents
Meta launched MLGym, which stands out as the first Gym-style framework built to evaluate AI research agents. This measurement tool comes with 13 different tasks that cover computer vision, natural language processing, reinforcement learning, and game theory. Teams can use MLGym to test how well agents perform and compare top models like Claude-3.5-Sonnet, GPT-4o, and Gemini-1.5 Pro. MLGym gives performance profile curves and AUP scores to track improvements between different agents and tasks.
Open Source Frameworks: LangChain, AutoGen, CrewAI
The world of agent development has several helpful frameworks. LangChain works as a modular toolkit with many integrations. It shines in complex workflows but might be too much for simple tasks. Microsoft's AutoGen does well with structured multi-agent teamwork thanks to its conversation-focused approach and simple interface. CrewAI brings a role-based system that keeps things simple and readable - making it great for quick prototypes and business uses. Your choice of framework should depend on task complexity, developer skills, scaling needs, and how well it fits with your current tech stack.
Ensuring Explainability and Transparency in Outputs
Trust in AI agents grows with transparent operations and good debugging options. You can add explainability by tracking and evaluating each step of agent reasoning. Your evaluation datasets should include at least 30 test cases per agent. These need to cover successes, edge cases, and failures. Critical systems need agents that "fail safe" instead of "fail fast" with proper error handling and clear escalation paths.
You can start using these transparency methods with Persana's AI agent platform, which includes built-in explainability features.
Continuous Learning and Feedback Loop Design
AI research agents get better over time with structured feedback. They learn by gathering insights from each interaction and fine-tuning their methods. This happens through updating existing models with new data and learning throughout their operational life. The agents learn from up-to-the-minute data analysis and human corrections through feedback loops. Memory systems help agents keep what they've learned while adapting to new situations.
Ethical Considerations in Autonomous Research Agents
Ethics become crucial as AI agents gain more independence. Clear roles and escalation paths help maintain accountability. Teams can reduce bias by broadening training data and using fairness-aware algorithms. Privacy stays protected through differential privacy techniques and purpose-bound consent. Human oversight remains important with defined autonomy limits and override options. Good AI systems should increase rather than replace human judgment.
Conclusion
AI research agents have changed how businesses collect and use information. This piece explores the detailed framework you need to build self-running research systems. These tools can scan thousands of online sources at once. They detect subtle buying signals and provide applicable information that human researchers might miss.
A successful research agent's foundation combines several key parts that work naturally together. These include perception modules, knowledge bases, reasoning engines, and action generators. This building-block approach helps systems handle complex tasks while staying accurate and adaptable. The systems learn from past interactions through both short-term and long-term memory.
You need careful planning to build your own research agent. Start by defining research goals using the SMART framework. Next, pick a foundation model that fits your needs. After you gather and clean up specific data for your field, adjust your model with PEFT or SFT techniques. The final steps involve creating good prompts and launching your agent with tools like Persana or CrewAI.
Your agent's success depends on how well it works with other systems. It should connect to knowledge bases, process immediate data, and work with your existing tools like CRMs or research platforms. The system becomes more efficient when research workflows start automatically based on specific events.
MLGym's framework offers standard ways to review and improve how well agents perform. Different tools serve different needs. LangChain, AutoGen, and CrewAI each offer unique benefits depending on what you want to achieve.
In spite of that, ethical issues remain crucial. Development must focus on accountability, reducing bias, protecting privacy, and human oversight. The best research agents increase human abilities instead of replacing them. This creates a partnership that combines machine speed with human wisdom.
AI research agents will change how organizations handle research tasks. Companies using these tools now will gain advantages through better efficiency, lower costs, and smarter decisions. Research's future lies in thoughtfully created autonomous agents that deliver reliable, useful insights exactly when needed.
FAQs
What are AI research agents and how do they work?
AI research agents are autonomous software systems that collect and analyze information from various sources. They use advanced algorithms to process vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and generate insights. These agents can scan thousands of online sources in real-time, detecting signals that human researchers might miss.
What are the key components of an AI research agent's architecture?
The core architecture of AI research agents typically includes a perception module for processing inputs, a knowledge base for storing information, a reasoning engine for analysis and decision-making, an action generator for executing tasks, and a learning module for continuous improvement based on feedback.
How can developers implement AI research agents in their projects?
Developers can implement AI research agents by first defining clear objectives, selecting an appropriate foundation model (e.g., GPT-4, PaLM 2), collecting and preprocessing domain-specific data, fine-tuning the model, and then deploying it using frameworks like AutoGen or CrewAI. Integration with external systems and implementing proper security measures are also crucial steps.
What are some best practices for developing scalable AI research agents?
Best practices include using benchmarking tools like MLGym to evaluate performance, leveraging open-source frameworks such as LangChain or AutoGen, ensuring explainability and transparency in outputs, implementing continuous learning mechanisms, and considering ethical implications throughout the development process.
What are the potential benefits of using AI research agents for businesses?
AI research agents can significantly improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance decision-making processes. They can automate up to 80% of manual research tasks, detect important signals within 24-48 hours, and help sales teams achieve 3-5x higher conversion rates by identifying opportunities at the right moment.

Create Your Free Persana Account Today
Join 5000+ GTM leaders who are using Persana for their outbound needs.
How Persana increases your sales results
One of the most effective ways to ensure sales cycle consistency is by using AI-driven automation. A solution like Persana, and its AI SDR - Nia, helps you streamline significant parts of your sales process, including prospecting, outreach personalization, and follow-up.

